Add documentation on how to develop woodpecker Co-authored-by: 6543 <6543@obermui.de> Co-authored-by: Lukas <lukas@slucky.de>
9.2 KiB
Development
Preparation
Install Tools
Go
Install Golang (>=1.16) as described by this guide.
make
GNU Make is a tool which controls the generation of executables and other non-source files of a program from the program's source files. (https://www.gnu.org/software/make/)
Install make on:
Node.js & Yarn
Install Node.js (>=14) if you want to build Woodpeckers UI or documentation.
For dependencies installation (node_modules) for the UI and documentation of Woodpecker the package-manager Yarn is used. The installation of Yarn is described by this guide.
Create a .env file with your development configuration
Similar to the environment variables you can set for your production setup of Woodpecker, you can create a .env in the root of the Woodpecker project and add any need config to it.
A common config for debugging would look like this:
WOODPECKER_OPEN=true
WOODPECKER_ADMIN=your-username
# if you want to test webhooks with an online SCM like Github this address needs to be accessible from public server
WOODPECKER_HOST=http://your-dev-address.com/
# github (sample for a SCM config - see /docs/administration/vcs/overview for other SCMs)
WOODPECKER_GITHUB=true
WOODPECKER_GITHUB_CLIENT=<redacted>
WOODPECKER_GITHUB_SECRET=<redacted>
# agent
WOODPECKER_SERVER=localhost:9000
WOODPECKER_SECRET=a-long-and-secure-password-used-for-the-local-development-system
WOODPECKER_MAX_PROCS=1
# enable if you want to develop the UI
# WOODPECKER_DEV_WWW_PROXY=http://localhost:3000
# used so you can login without using a public address
WOODPECKER_DEV_OAUTH_HOST=http://localhost:8000
# disable health-checks while debugging (normally not needed while developing)
WOODPECKER_HEALTHCHECK=false
# WOODPECKER_LOG_LEVEL=debug
# WOODPECKER_LOG_LEVEL=trace
O-Auth
Create an O-Auth app for your SCM as describe in the SCM documentation. If you set WOODPECKER_DEV_OAUTH_HOST=http://localhost:8000 you can use that address with the path as explained for the specific SCM to login without the need for a public address. For example for Github you would use http://localhost:8000/authorize as authorization callback URL.
Developing with VS-Code
You can use different methods for debugging the Woodpecker applications. One of the currently recommend ways to debug and test the Woodpecker application is using VS-Code or VS-Codium (Open-Source binaries of VS-Code) as most maintainers are using it and Woodpecker already includes the needed debug configurations for it.
As a starting guide for programming Go with VS-Code you can use this video guide:
Debugging Woodpecker
The Woodpecker source code already includes launch configurations for the Woodpecker server and agent. To start debugging you can click on the debug icon in the navigation bar of VS-Code (ctrl-shift-d). On that page you will see the existing launch jobs at the top. Simply select the agent or server and click on the play button. You can set breakpoints in the source files to stop at specific points.
UI development
To develop the UI you need to install Node.js and Yarn. In addition it is recommended to use VS-Code with the recommended plugin selection to get features like auto-formatting, linting and typechecking. The UI is written with Vue 3 as Single-Page-Application accessing the Woodpecker REST api.
The UI code is placed in web/. Change to that folder in your terminal with cd web/ and install all dependencies by running yarn install. Start the UI locally with hot-reloading by running: yarn start. To access the UI you now have to start the Woodpecker server.
For this you have to add the line WOODPECKER_DEV_WWW_PROXY=http://localhost:3000 to your .env config and start the server after that as explained in the debugging section.
The UI will now be served under http://localhost:8000 (don't access the UI from port 3000 as that only show the UI without access to the actual api).
Tools and frameworks
The following list contains some tools and frameworks used by the Woodpecker UI. For some points we added some guidelines / hints to help you developing.
- Vue 3
- use
setupand composition api - place (re-usable) components in
web/src/components/ - views should have a route in
web/src/router.tsand are located inweb/src/views/
- use
- Windicss (similar to Tailwind)
- use Windicss classes where possible
- if needed extend the Windicss config to use new classes
- Vite (similar to Webpack)
- Typescript
- avoid using
anyandunknown(the linter will prevent you from doing so anyways 😉)
- avoid using
- eslint
- Volar & vue-tsc for type-checking in .vue file
- use the take-over mode of Volar as described by this guide
Documentation development
The documentation is using docusaurus as framework. You can learn more about it from its official documentation.
If you only want to change some text it probably is enough if you just search for the corresponding Markdown file inside the docs/docs/ folder and adjust it. If you want to change larger parts and test the rendered documentation you can run docusaurus locally. Similarly to the UI you need to install Node.js and Yarn. After that you can run and build docusaurus locally by using the following commands:
cd docs/
yarn install
# build plugins used by the docs
yarn build:woodpecker-plugins
# start docs with hot-reloading, so you can change the docs and directly see the changes in the browser without reloading it manually
yarn start
# or build the docs to deploy it to some static page hosting
yarn build
Testing & linting code
To test or lint parts of Woodpecker you can run one of the following commands:
# test server code
make test-server
# test agent code
make test-agent
# test cli code
make test-cli
# test datastore / database related code like migrations of the server
make test-server-datastore
# lint go code
make lint
# lint UI code
make lint-frontend
# test UI code
make test-frontend
If you want to test a specific go file you can also use:
go test -race -timeout 30s github.com/woodpecker-ci/woodpecker/<path-to-the-package-or-file-to-test>
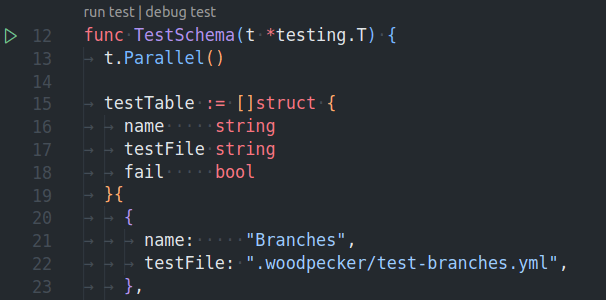
Or you can open the test-file inside VS-Code and run or debug the test by clicking on the inline commands:
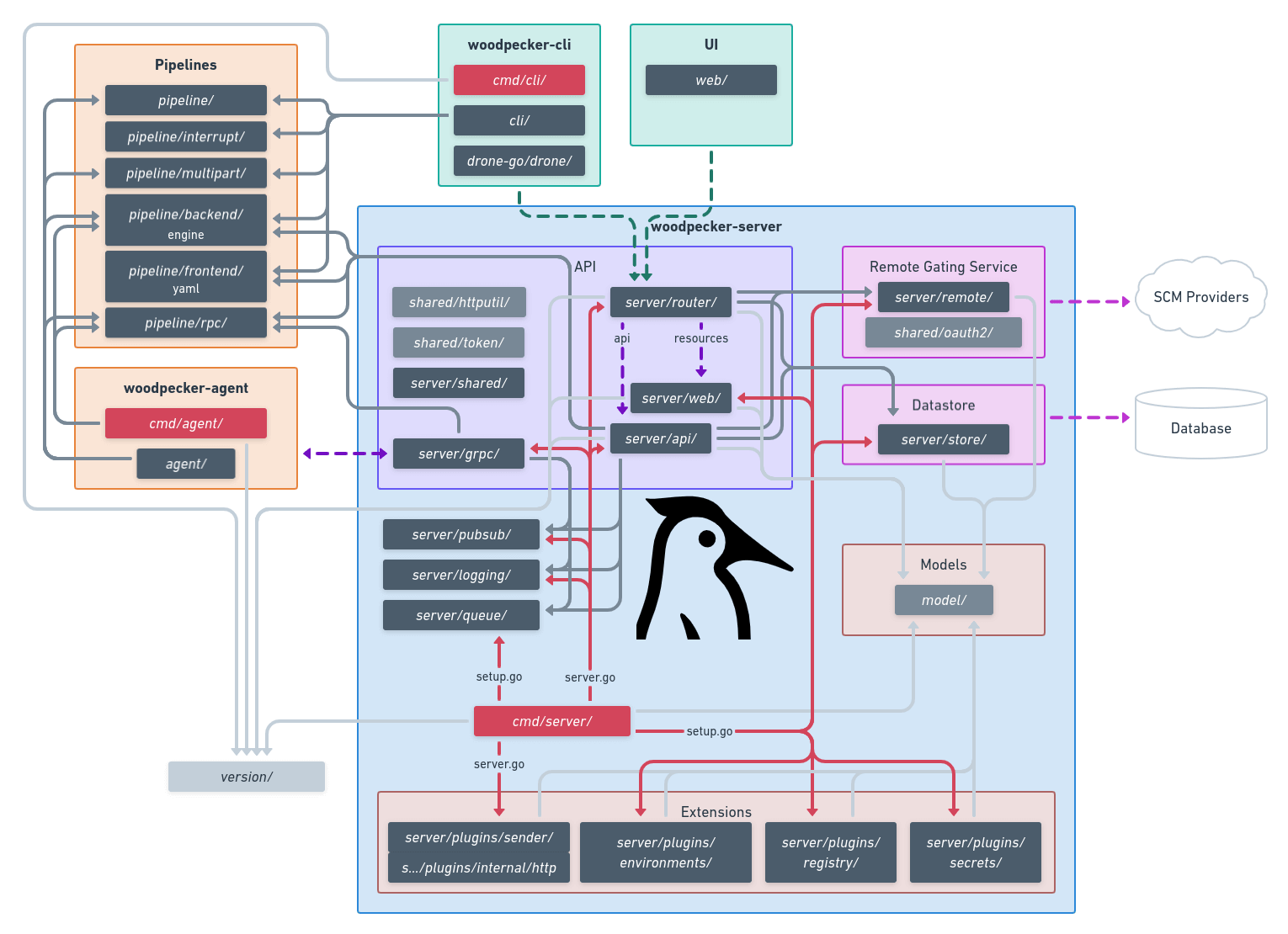
Package architecture of Woodpecker
Run applications from terminal
If you want to run a Woodpecker applications from your terminal you can use one of the following commands from the base of the Woodpecker project. They will execute Woodpecker in a similar way as described in debugging Woodpecker without the ability to really debug it in your editor.
# start server
$ go run ./cmd/server
# start agent
$ go run ./cmd/agent
# execute cli command
$ go run ./cmd/cli [command]
Add new migration
Woodpecker uses migrations to change the database schema if a database model has been changed.
:::info
If you add a new property to a model, you dont have to do anything,
the column will be created based on the xorm tag automaticaly.
If you add a new model, you only have to add it to the syncAll() function at
server/store/datastore/migration/migration.go to get a table created.
:::
If a developer for example removes a property Counter from the model Repo in server/model/ they would need to add a new migration task like the following example to a file like server/store/datastore/migration/004_repos_drop_repo_counter.go:
package migration
import (
"xorm.io/xorm"
)
var alterTableReposDropCounter = task{
name: "alter-table-drop-counter",
fn: func(sess *xorm.Session) error {
return dropTableColumns(sess, "repos", "repo_counter")
},
}
:::warning
Do not sess.Begin(), sess.Commit() or sess.Close() the session, it is managed from outside.
:::
To automatically execute the migration after the start of the server, the new migration needs to be added to the end of migrationTasks in server/store/datastore/migration/migration.go.
:::tip Woodpecker uses Xorm as ORM for the database connection. If you can find its documentation at gobook.io/read/gitea.com/xorm. :::